A. Tejero, D. Manzano, P.I. Hurtado
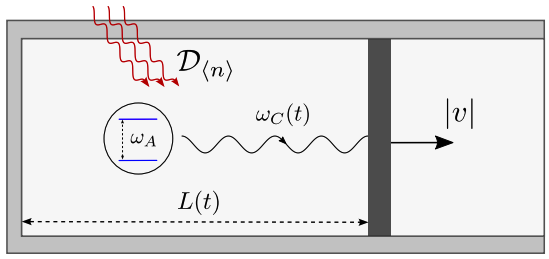
The possibility of efficiently converting heat into work at the microscale has triggered an intense research effort to understand quantum heat engines, driven by the hope of quantum superiority over classical counterparts. In this work, we introduce a model featuring an atom-doped optical quantum cavity propelling a classical piston through radiation pressure. The model, based on the Jaynes-Cummings Hamiltonian of quantum electrodynamics, demonstrates the generation of mechanical work through thermal energy injection. We establish the equivalence of the piston expansion work with Alicki’s work definition, analytically for quasistatic transformations and numerically for finite time protocols. We further employ the model to construct quantum Otto and Carnot engines, comparing their performance in terms of energetics, work output, efficiency, and power under various conditions. This model thus provides a platform to extract useful work from an open quantum system to generate net motion, and sheds light on the quantum concepts of work and heat.
